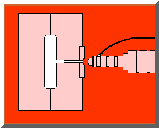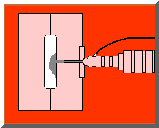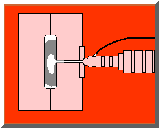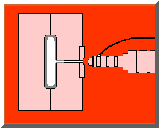
Injection molding companies are now regularly using a procedure called Gas Assisted Molding utilizing nitrogen gas to produce unfilled hollowed out gaps within the plastic-part the injection mold creates. At the finish of the filling stage, the gas (N2) is being injected to the still liquid core of the molding. At this time the nitrogen gas requires the most convenient road to minimum resistance (very similar to water does); after which takes the place of the heavy liquefied things with gas-fulled segments. At this point there is pressure applies by the gas which compresses the plastic resin strongly to the injection mold outside, all the while adjusting for the amount of volume and downsizing; continuous till the plastic part becomes solid. Eventually, the gas is vented to atmosphere or re-cycled.
 The gas-assisted injection molding process has become a practical process for over two decades with a lot of companies being concerned about patenting issues and royalty-fees. During the last couple of years, among the unique patents have run out. And now, gas-assist injection molding is broadly used. Design technicians and processors alike are finding that this technology is usually an enticing option for certain applications and offers many benefits. It will be the duty of the manufacturer to establish that their practice or technologies is not covered by current patents.
The gas-assisted injection molding process has become a practical process for over two decades with a lot of companies being concerned about patenting issues and royalty-fees. During the last couple of years, among the unique patents have run out. And now, gas-assist injection molding is broadly used. Design technicians and processors alike are finding that this technology is usually an enticing option for certain applications and offers many benefits. It will be the duty of the manufacturer to establish that their practice or technologies is not covered by current patents.
Procedures have been completely engineered by which inert gas nitrogen is injected to the still molten plastic in the mould cavity. Operating from the inside of the part shape, the gas fills up the component and counteracts the effects of the material shrinkage.. The effect is to keep an internal pressure on the material until it solidifies and skins at the mould cavity surface.
Primary Applications of Gas Assisted Moulding
The main two applications of Gas Assisted Moulding are to either inject the gas into the component cavity (internal gas injection), or to use the gas on the outside surface, but still within the mould cavity, to consolidate the component (external gas injection).
Central Gas Assist Injection Molding Features – Applied the Most
The pros are wide ranging starting with considerable cost reductions resulting from: 1. Decrease in molded plastic weights, and therefore price of product. 2. Decrease in molding time period cycles, and therefore expense of manufacturing. 3. Lessened in-mold pressures, and thus significantly less wear on molds.
More benefits include the use of the gas as a means of transmitting pressure uniformly throughout the molding, plus elimination of sink marks. The avoidance of plastic packing from the molding equipment and reduced in-mold pressures by up to 70%; hence decreased press lock forces which allows larger moldings on smaller units. It’s also well worth pointing out the reduced electrical power consumption, lowered molded in stress, and therefore enhanced dimensional stability without deformation.
The simplest way Gas Assist Injection Molding Will Manage To Benefit Your Small Business
Product financial savings (weight, cost) for thick-walled parts up to forty-percent
The combined advantages of not packing a moulding tend to be significantly less substance is put to use. Through not having to group the content, plus in heavier elements the resultant hollow core, can conserve around close to forty percent to the Reduced Cycle times by 50% or more when compared to standard injection molding of thick-walled parts. Another major benefit is the reduction in machine cycle times that can be achieved. With no molten core to strengthen, the material within the mold cavity stiffens faster as a result allowing the component to be ejected faster.
Using gas assist molding allows engineers to develop thin-walled components. It’s moreover suitable for building solid but hollow portions to thin-walled products. Because the component could be injected with little tonnage clamping pressures, the skinny partitions of the component continue to be together and secure with gas assist injection molding.
The complete consequence of gas assist molding? More advanced parts, more rapidly cooling periods, lowered cycle time and most significantly, reduced cost compared to regular molding techniques.
Gas Injection Molding Benefits
Ideally suited to numerous companies and challenges, gas assisting molding is an optimum remedy for materials which might be tube or rod shaped with a hollow center, parts which might be structural such as panels and covers, and materials which contain equally lean and thicker portions.
- Decrease secure strains
- Enhanced controlling pressures influence
- High flexural solidity and torsion firmness
- Minimal inner pressure levels and small warp-age for thick and thin wall structure combinations (uniform shrinkage and stress)
- Reduction of sink scars
- Pattern independence
- A lot fewer weld outlines thanks to less injection insertion points
- Extended movement lengths or decrease amount of injection points essential for large thin-walled shaped parts for the reason that gas channels behave as movement leaders